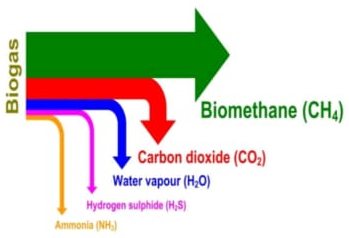
Components Of BIO Gas
CBG Production Technology
Biogas is a product from the process of degradation of organic matter by anaerobic bacteria. The biogas generation process consists of four subsequent chemical and biochemical reactions i.e. Hydrolysis reaction, Acidogenesis reaction, Acetogenesis reaction and Methanogenesis reaction.
Hydrolysis reaction decomposes organic molecule such as carbohydrates, proteins and fats into glucose, amino acids and fatty acids, respectively. Acidogenesis converts those generated small organic molecules to volatile organic acids with help from bacteria. During the Acetogenesis process, bacteria in the acetic group digests volatile organic acids and releases acetic acid. Lastly, anaerobic bacteria in the methanogenic producing bacteria group will complete the Methanogenesis process by converting acetic acid to methane gas and other gases like carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide.
Hydrogen sulfide is a corrosive gas. Presence of carbon-dioxide in the bio-gas reduces its calorific value. Hence the bio-gas needs to be purified. Various technologies are used for removal of hydrogen sulfide.
© Mukesh Walia & Company. All Rights Reserved. Website Designed & Developed By Cyberxel
